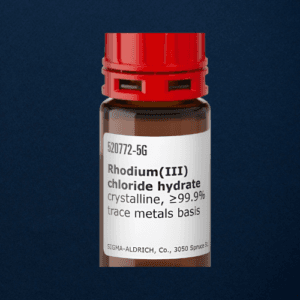
Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate
Price range: £500.00 through £9,000.00
Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate is a valuable red-brown compound with significant uses in catalysis, hydrogenation, and electroplating. It is known for its stability, high reactivity, and catalytic efficiency in chemical processes.
Description
Rhodium(III) Chloride Hydrate: Overview and Applications
Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate is a highly valued chemical compound consisting of rhodium in its +3 oxidation state, combined with chloride ions and water molecules. As a transition metal complex, it is one of the most important rhodium-based compounds used in various industrial, chemical, and catalytic applications. Rhodium itself is a rare, precious metal known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high melting point, and excellent catalytic properties, making Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate an important substance in a range of chemical processes.
Properties of Rhodium(III) Chloride Hydrate
Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate typically appears as a red-brown crystalline solid. It is highly soluble in water and can form various coordination complexes, which are often used in catalytic reactions. The presence of water molecules in its structure gives it unique characteristics, such as increased stability and solubility, which are key for its catalytic activity. Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate is usually prepared by reacting rhodium with hydrochloric acid, and its complex chemistry makes it valuable in both laboratory research and industrial applications.
Uses and Applications
- Catalysis: Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate is widely used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. It is particularly useful in catalytic reactions like hydrogenation, hydroformylation, and carbonylation. Its ability to facilitate reactions without being consumed in the process is what makes it a valuable component in chemical manufacturing.
- Hydrogenation Reactions: Rhodium catalysts are essential in hydrogenation processes, where unsaturated organic compounds are converted into saturated ones. This is crucial in the production of various chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals.
- Fine Chemical Synthesis: Due to its high activity and selectivity, Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate is employed in the production of fine chemicals and specialty materials. It is also utilized in the synthesis of important compounds in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries.
- Electroplating: Rhodium, in its chloride form, is also used in electroplating processes to apply thin coatings of rhodium onto various substrates, typically for aesthetic purposes or to increase corrosion resistance in components.
Safety and Handling
Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate, like other rhodium compounds, should be handled with care, as it can be toxic if inhaled or ingested. Appropriate safety measures, such as wearing gloves and using fume hoods, are recommended when working with this compound in laboratory or industrial settings. It is also important to avoid direct contact with the eyes or skin to prevent irritation.
Specifications and Chemical Composition
- Chemical Formula: RhCl₃·xH₂O (where x represents the number of water molecules)
- Appearance: Red-brown crystalline solid
- Molecular Weight: Varies depending on the hydrate form (approximately 289.3 g/mol for RhCl₃)
- Solubility: Soluble in water and other polar solvents
Features
- High Catalytic Efficiency: Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate is known for its excellent catalytic properties, making it highly valuable in industrial catalysis.
- Stability: The hydrated form of rhodium chloride offers enhanced stability compared to anhydrous forms, especially in aqueous environments.
- Reactivity: It reacts readily in various chemical processes, including hydrogenation and carbonylation reactions.
Conclusion
Rhodium(III) chloride hydrate is an indispensable compound in modern chemistry, known for its exceptional catalytic properties and wide range of applications, particularly in organic synthesis and electroplating. Although it is used in small quantities due to the rarity of rhodium, its high efficiency and versatility make it a critical material in industrial and research settings. Proper handling and storage are essential to ensure safety and optimal use in chemical processes.
Additional information
| Weight | 100g, 10g, 20g, 50g |
|---|